Design Enabling Behavior Change
Human behavior is affected by various forms of persuasion. Understanding the components that make for a persuasive message is a critical focus of professions ranging from advertising to politics and even public health. e.g.- A major goal for advertising is to have an enduring emotional impact on an audience to influence them to buy the product. This is achieved through a process of co-creation in which consumers integrate advertising content with their own attitudes, beliefs, and values to produce the meaning of belonging with the product.
In the field of UX design, understanding these principles is equally necessary. There are 3 main drivers of persuasion:
-
- Need to Belong
The first rule of persuasion plays on the human need to belong. The need to conform to a group. Most common example: When it’s raining in the city, a group of bikers have taken shelter under a bridge/ flyover. One person decides that he can drive in the reduced force of rain and gets out of the shelter. When he drives off – everybody, without giving it a thought, drive off too. There are so many such similar examples not in physical but, in the digital world as well. e.g.- 4 people from your list ‘Like’ a picture on Facebook and involuntarily you ‘Like’ the picture too.
-
- Power of Stories
“We dream in narrative, day-dream in narrative, remember, anticipate, hope, despair, believe, doubt, plan, revize, criticise, construct, gossip, learn, hate and love by narrative.” – Barbara Hardy, a British scholar.
The secret to a more effective communication is better stories. The power of stories becomes an important principle to look at. Managers, leaders, influencers persuade us using the power of stories. One can engage, entertain and inspire with the power of stories.
-
- Carrots and Sticks
This is incentives or rewards and punishment. These two are the very basic reasons for motivation to take any form of action. These are the lessons learned from behavioral economics – the fascinating science of rewards and punishments. An easy but high-powered strategy for setting and achieving goals already being used by successful companies and individuals across the globe.
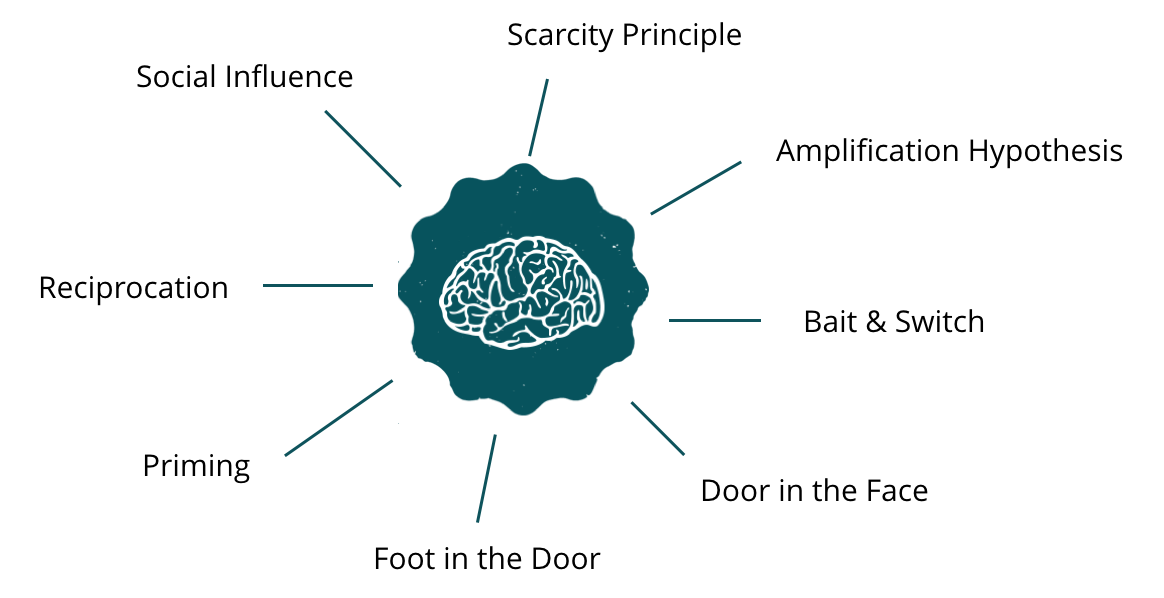
Principles of Persuasion:
-
- Social Influence
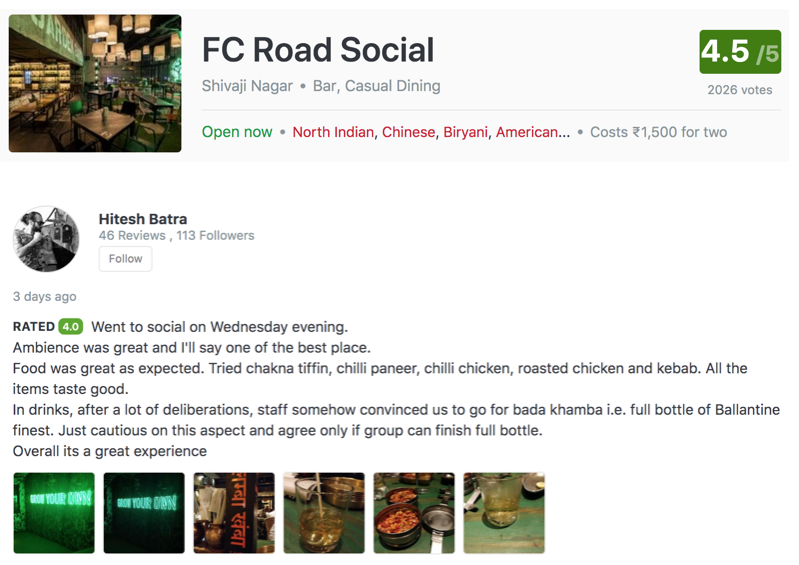
It is common knowledge that in today’s world, we often take decisions based on what is more popular socially. Here’s an example of how we choose to go to a restaurant based on the reviews of earlier customers.
-
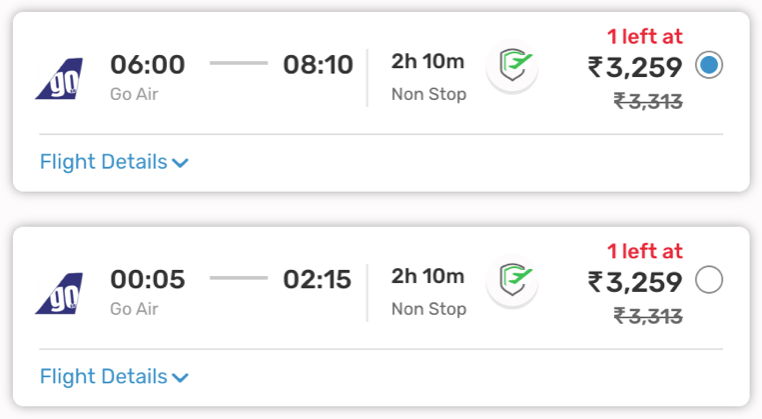
- Scarcity Principle
Companies use this principle, to provoke customers to take action sooner than anticipated, where with more time, there is more scope for the customer to drift away from the website exploring more options. e.g.- makemytrip.com
-
- Amplification Hypothesis
If a credible source provides information wherein they amplify the good part, people find it very easy to believe in it. e.g.- Ola Restrooms.

-
- Bait & Switch
Typically, at sales in retail stores. When it says, upto 85%, technically only 8-10% goods have 80-85% discount. Yet the influence of the big number used as primary message in the advertising, makes the customer rush for the sale and buy products that do not have the promised discount.

-
- Door in the Face
Ask for a uncomfortably big favour, impossible for anyone to say yes to easily, then ask the smaller favour you actually want. Here’s a classic example of that –
-
- Foot in the Door
Capturing attention by claiming minimal effort by the customer and adding steps to increase their curiosity leading them to buy the product. Reciprocity also plays a part here, free of charge services making the customers feel obliged to buy in to their services.
-
- Priming
Influencing the customer such that, they start associating the symbol and colour of the brand with hunger, comfort, instant gratification etc. MacDonald’s campaigning at its best.

-
- Reciprocation
Another example where reciprocation principle is used.

-
- Conversion Theory
12 Angry Men. The classic movie, is a perfect example where a dissenting juror in a murder trial manages to convince and slowly turn others that the case is not obviously clear as it seemed in the court.

Importance of Memory in Design
While there are many factors considered to determine our interactions with the outside world, one of the most important is memory. Without memory, we could not determine, process or recognize or rate our experiences as good or bad. Memory of how a brand treats you, is one of the crucial factors in a customer’s decision making process.
The capacity of human brain is 2.5 petabytes. If you make a movie out of these 5 petabytes of memory and play it, it will keep on playing for 300 years! Such is the vastness of human capacity of brain. Though, our brain has multiple types of memory. Working/ short term memory, long-term memory.
Human brain has the tendency to remember the start and end points of any experience. This phenomena is called primacy and recency. These should be considered when designing an experience for the user. Similarly, Miller’s law, recognition principles in case of long-term memory and among others should be used when designing.
It is important that we dig deep and make the most of this factor to deliver a connected physical and digital experience. The question is, with the influence design has on memory and human behaviour, how do you want to make an impact?
Amplify your brand presence with the best UX design studio that truly aligns your needs with those of your consumers! Get in touch with us at YUJ Designs, today!