As an interaction designer your primary responsibility is to ensure that your designs meet the business goals as well as users needs and expectations. Business stakeholders may not know the nuances of design but would show zealous participation in design reviews. They may provide design suggestions or changes that may jeopardise the user experience of the product as well as your credibility.
What should designers do to safeguard this situation?
Design is meant for people to view, understand and interact. That means human brain is processing information that is presented. Thus unlike arts, design came into being more as a scientific practice. Any piece of science warrants justification. Hence, designers’ need to be well-versed with rationale – one that explains the logic behind design decisions becomes more critical to business.
Through this blog, I would like to bring your attention to some of these human cognition principles that become the base for making human computer interactions reliable and justifiable.
Keystroke Level Model
KLM predicts execution time for a particular task based on time required for each low level actions. These actions include homing (moving hand to mouse or keyboard), key press, pointing, thinking time.
For e.g. in a study participants were asked to rate their views for 3 questions. For which the time required was calculated with KLM model.
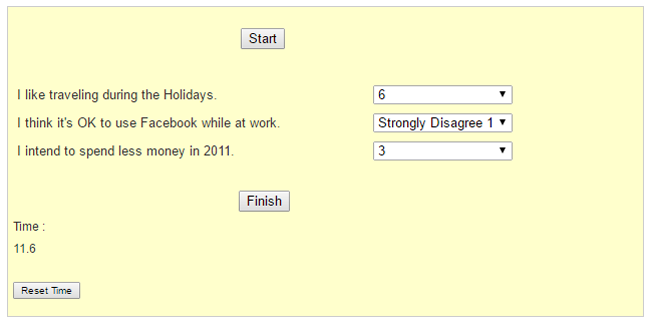
Design solution 1 : Users required 8 clicks (11.6 sec) to complete the task with the first design solution.
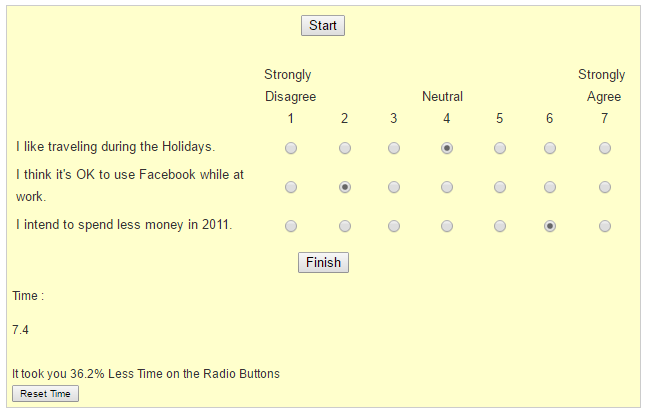
Design solution 2 – Time Reduced by 36.2% : Users required 5 clicks (7.4 sec) to complete the task with the second design solution.
Behaviour Model for Persuasive Design
This model helps designer understand key factors for determining users’ behaviour. There are 3 important factors for successful completion of tasks –
Motivation : Motivation can help user create desire or need to do the task. Motivation can be pleasure or pain, hope or fear, or social acceptance or rejection.
E.g. People are motivated by fear when they see warning on deletion of files on computer.
Ability : Ability is simplicity with which users can perform the tasks. Simpler the product to use/ do the task users will be more inclined to complete the task. Ability helps designer to understand how the behavior of users can be made simple? Simplicity (Ability) can be in terms of Time, Money, Physical efforts, brain cycles, Social deviance and non-routine.
E.g. Users’ ability to quickly search something based on actions seen on the screen
Triggers : Trigger is something that tells people to perform some action. In a digital user interface, it can be a button or a textbox or a link. It is a cue for users for target behavior to occur. Different types of trigger such as Spark, Facilitator and Signal will act in different ways provided users have motivation and ability.
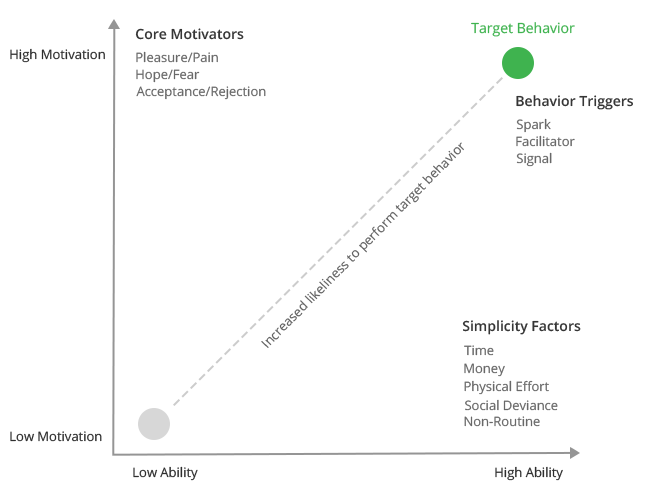
At a glance : Behavior Model for Persuasive Design
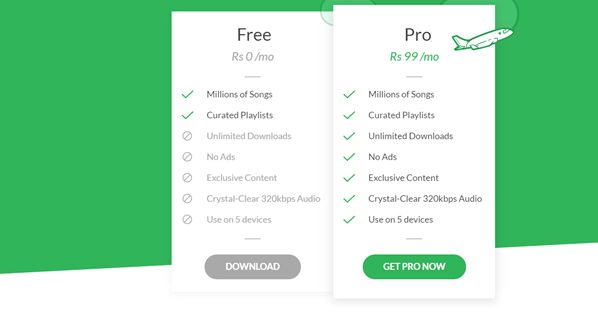
Example – Behavior Model for Persuasive Design : The page uses different elements of Behavior model to entice users to purchase product. Here motivation (Pleasure) is to get all the benefits. Ability (Money) to get subscription for value proposed. Trigger (Signal) is indicated with button that users can purchase product with single click.
Hick’s Law
Hick’s law tells that reaction time will increase exponentially as number of options to choose from increases. This broader definition of Hick’s law will be insufficient, as the context of where it is applied is equally important.
In day to day usage of digital systems, users will come across multiple actions or menus to choose from. What makes a difference is applying hick’s law to well categorized information and actions specific to it.
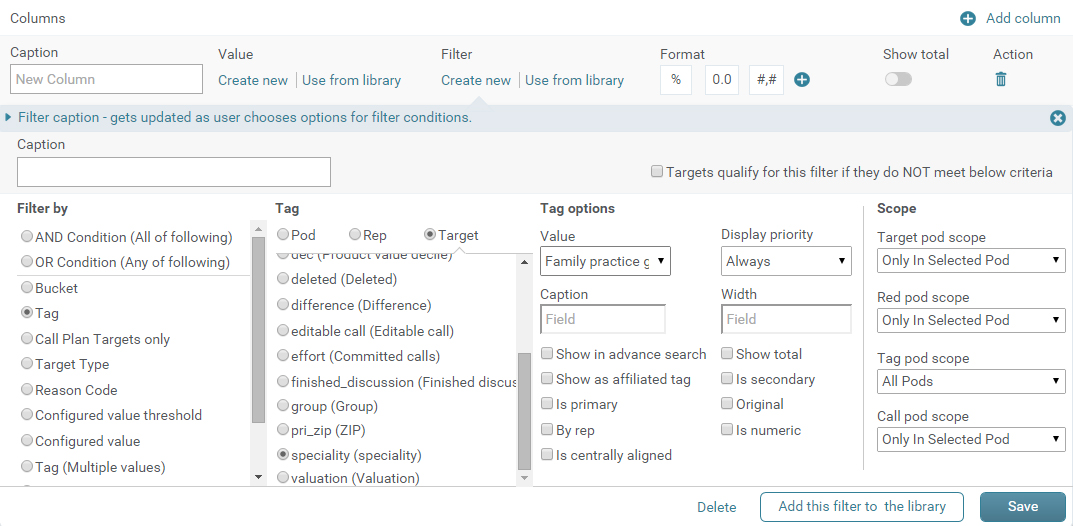
Filters : This is example of complex filters, where users have to select multiple options from different categories to see desired entities. Time required to select these options can be reduced by correctly categorizing it and following particular order based on priority or requirement
Online shopping sites are best examples for this. Users can quickly search required products from the thousand different product categories. While buying, users can quickly narrow down to choices with the help of correct categorization and grouping.
References
Amplify your brand presence with the best UX design studio that truly aligns your needs with those of your consumers! Get in touch with us at YUJ Designs, today!